SẢN PHẨM
Năng lực R&D sản phẩm hàng đầu
VÒNG BI CẦU TIẾP XÚC GÓC BỐN ĐIỂM
Angular contact ball bearings are especially good for taking combined loads, i.e. simultaneously acting radial and axial loads. The axial load carrying capacity of these bearings increase with contact angle increasing. A bearing contact angle is defined as the angle between a radial plane perpendicular to the bearing axis and the line connecting the two contact points of a ball with the inner and outer ring proves, so that the load resultant is transmitted by one bearing rib to the other alone. Large or small contact angles are indicated by different designation suffixes respectively.
HRB angular contact ball bearings include:
– Single-row angular contact ball bearings
– Double-row angular contact ball bearings
– Four-point contact ball bearings
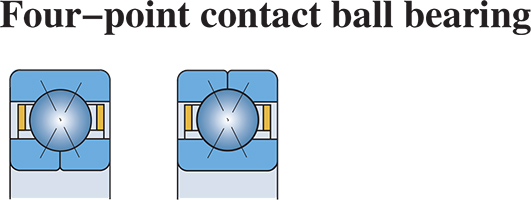
Four-point contact ball bearings are a kind of single row angular contact ball bearings which can accommodate high axial loads in either direction. The occupied space of these bearings is smaller than that of the double row bearings. Listed in the following table, with a contact angle of 35°, the four-point contact ball bearings have a split inner ring which allows a large complement of balls to be filled in so as to achieve high load carrying capacity in axial direction. These bearings are separable, that is the two halves of the inner ring and the unit of the outer ring, cages and balls can be mounted individually.
Locating groove
Four-point contact ball bearings are mainly used to take axial loads, and in many applications they are used as a thrust bearings to adapt a certain amount of axial loads, loosely mounted in the housing.
Large four-point contact ball bearings with outside diameter equal to or greater than 160 mm have two locating grooves (N2 design) on the outer ring for fixing the outer ring and avoiding its rotating.
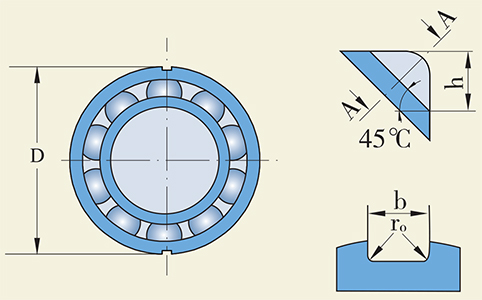
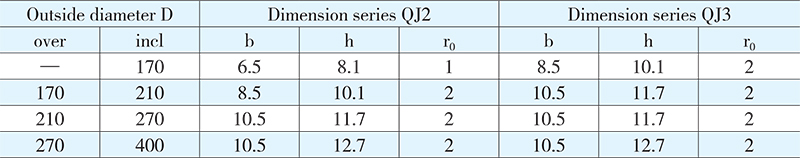
Dimensions of locking grooves are given in Table 1.
Table 1 (mm)
Misalignment
Four-point contact ball bearings can only accommodate limited errors of alignment between the inner and outer rings. Just as that of deep groove ball bearings, there is a complicated relationship between the factors which determine the allowable values of angular misalignment. Precaution: angular misalignment could induce additional noise in the bearings.
Where the four-point contact ball bearings as a thrust bearing is mated with a radial bearing, they must be loosely fitted in the housing with a radial clearance after mounted, and angular misalignment between the inner and outer rings is not allowed.
Tolerances
HRB four-point contact ball bearings of standard design are manufactured to normal tolerances, Some sizes of the bearings of higher accuracy (tolerance class P6) are also available, contact HRB technology department before ordering.
Axial internal clearance
HRB four-point contact ball bearings of standard design have normal axial clearance. Bearings with larger or small axial clearance are also supplied on request for check by HRB techmology department before ordering.
Values for axial internal clearance are obtained from the following table, bearings having zero measuring load prior to mounting.
Axial internal clearance for four-point contact ball bearings
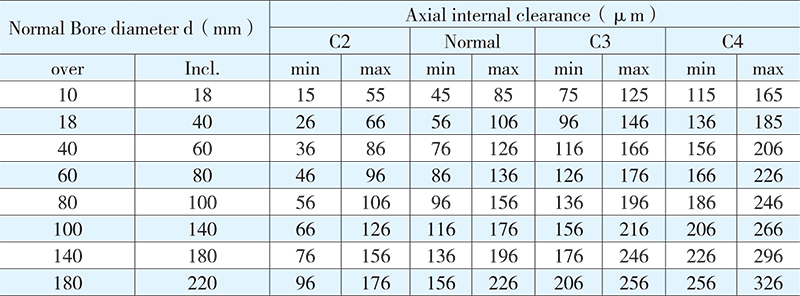
Radial clearance ≈ 0.7 axial clearance
Cages
HRB four-point contact ball bearings of standard design are mated with machined solid brass cage rided by the outer ring, some of them with cage of glass-fibre reinforced nylon 66 which has to be check with HRB before ordering.
Minimum rolling bearing load
In order to keep proper running of ball or roller bearings, the minimum required loads have to act on them including four-point contact ball bearings at least, or else during high speed running the mass forces of the balls and cage and the inadequate lubricant resistance may generate a harmful sliding between the balls and raceways, easy to lead to bearing damage.
Considering such a situation, the minimum required load is estimated from the following equation:
Fam = ka × C0/1000 × (n × dm/100000)2
where:
Fam: minimum axial load, N
ka: minimum axial load factor
=1.0, for QJ2 series bearings
=1.1, for QJ3 series bearings
C0: basic static load rating, N, see bearing tables
n: bearing speed, r/min
dm: bearing mean diameter
=0.5(d+D), mm
In general, the external force always goes beyond the minimum required load. If not, an additional load has to be exerted, by way of a spring, etc.
Equivalent dynamic bearing load
Where four-point contact ball bearings with a contact angle of 35o are used as locating bearings to accommodate both axial and radial loads, the equivalent dynamic bearing load can be obtained from the following equation:
P = Fr + 0.66Fa , for Fa/Fr ≤ 0.95
P = 0.65Fr + 1.07Fa , for Fa/Fr>0.95
It must be beared in mind that the ball set can approach to desirable running in the four-point contact ball bearings only when the ball touches a raceway at two points, i.e. in the case of Fa ≥ 1.27Fr.
Where the four-point contact ball bearings is as a thrust bearing to be mated with the other bearing, the bearing must be loosely fitted in the bearing housing when mounted. In such a case, the equivalent dynamic bearing load should be:
P = 1.07Fa
Equivalent static bearing load
Four-point contact ball bearings with a contact angle of 35°.
P0 = Fr + 0.58Fa
CATALOG VÒNG BI CẦU TIẾP XÚC GÓC BỐN ĐIỂM HRB