SẢN PHẨM
Năng lực R&D sản phẩm hàng đầu
Năng lực R&D sản phẩm hàng đầu

VÒNG BI CẦU CHẶN MỘT HƯỚNG
Single direction thrust ball bearings are separable, composed of a shaft washer, a housing washer and a cage-ball assembly, convenient for mounting and dismounting. The so called shaft washer is fitted with shaft tightly and the so called housing washer mated with the shaft loosely. Single direction thrust ball bearings which can only take axial loads in one direction and locate the shaft in one direction must not be loaded radially.
Their limiting speeds are comparatively lower because the radial shaft-to-housing floating couldn’t be restrained. If the axis of the shaft cannot coincide with the axis of the bearing housing bore or the axis of the shaft is not perpendicular to the housing support surface, the thrust bearing must be worn out earlier. In such a case, thrust ball bearings with sphered seatings are preferable, so as to compensate the errors of alignment between the housing and shaft.
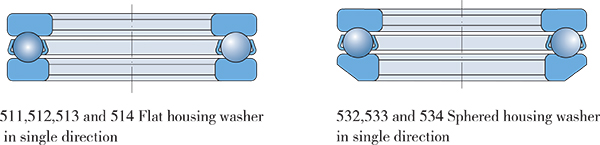
Dimensions
The boundary dimension of the thrust ball bearings listed in the following bearing tables are in conformity with ISO104.
Tolerances
HRB basic thrust ball bearings generally have P0 class tolerances, On customer’s demand, the bearings can be supplied upto P6, P5 and P4 class tolerances. Dimensional tolerance are also obtained from the tolerance tables for thrust bearings.
Cages
HRB thrust ball bearings are accompanied with two kinds of cages, pressed steel or machined brass, specified in the table below.
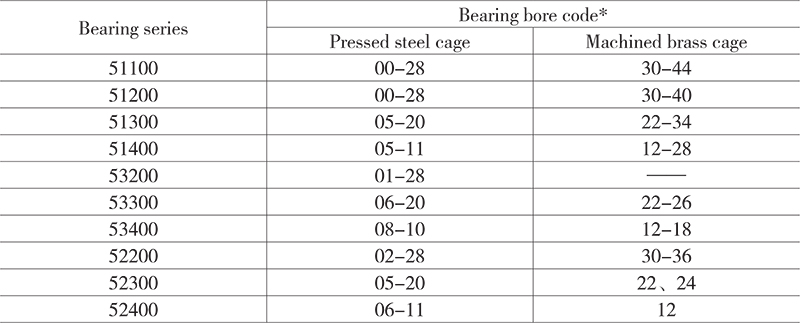
* The listed bearing bore code is the last two figures in the bearing designation, so that the bearing bore size can be obtained from the code multiplied by 5.
Minimum rolling bearing load
During high speed running, the inertia forces of the cage and balls may cause sliding between the ball-to-raceway contacts in the thrust ball bearings, easy to generate heat and wear on working surface. In order to avoid sliding of ball to the raceway, a certain minimum axial load Famin has to be exerted on the thrust ball bearing while working.
Famin ≥ A(nmax/1000)2
where:
Famin: minimum required axial load, kN
A: minimum axial load factor, listed in the bearing tables
nmax: maximum working speed, rpm
In general the bearing support mass adding external forces always goes beyond the minimum required axial load. If not, an additional preload has to be exerted, for example by a spring.
Equivalent static bearing load
Single and double direction thrust ball bearings: P0 = Fa
Equivalent dynamic bearing load
Single and double direction thrust ball bearings: P = Fa