SẢN PHẨM
Năng lực R&D sản phẩm hàng đầu
Năng lực R&D sản phẩm hàng đầu

VÒNG BI CẦU RÃNH SÂU MỘT DÃY – VÒNG BI CẦU
HRB deep groove ball bearings are of non-separable type, in which the depth of the inner and outer ring grooves enables the bearings to accommodate radial loads, axial loads in either direction and combined loads, suitable at high speeds.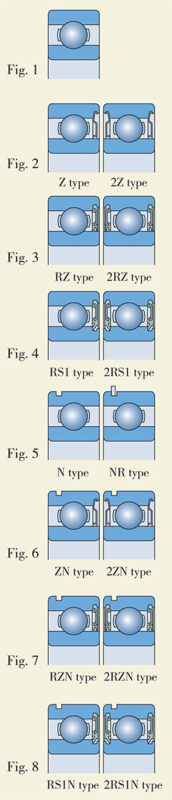
Single row basic design bearings
HRB manufactures different series of deep groove ball bearings of open basic design, shown Fig 1. There is no any special requirement of mounting and sealing for such bearings, widely used in machinery.
Bearings with shield(s) or seal(s)
In addition to open basic groove ball bearings, HRB also produces closed deep groove ball bearings to avoid independent relubrication as standard products to supply, i.e., with one shield (type Z), or two shields (type 2Z); with one seal (type RZ) or two seals (type 2RZ); RS1 and 2RS1 rubbing sealed bearings can be supplied as well. These bearings are filled with the correct quantity of grease while manufacturing, suitable for lower speeds. They must not be washed and relubricated before being mounted. This grease can keep bearings from rust and leaking. These bearings can serve many kinds of machines, especially suitable for poor environment which needs bearing to have self-sealed function. The quantity of grease is related to the bearing dimension and usage conditions, i.e., about 25 to 35% of the free space is filled with grease.
Bearings with snap ring groove and snap ring
HRB produces deep groove ball bearings with snap ring groove and snap ring in the outer ring (shown in Fig.5~8), which simplify the design of their housings, that is the bearing is located in the housing by snap ring. These bearings can be selected for the use of restricted space. The sizes of snap ring grooves and snap rings are listed in bearing tables.
Low noise bearings
HRB supplies low noise bearings, such as acceleration level low noise bearings with designation suffix Z1, Z2 and Z3, much lower with designation suffix Z4 to meet the silent requirement of air conditioner motors. High speed level low noise bearings can also be supplied, with designation suffix V1,V2 and V3. can make more variances in every type deep groove ball bearings, on customer`s request. Various tolerance classes and vibration levels of these bearings can be provided as well.
Dimensions
The boundary dimensions of deep groove ball bearings listed in bearing tables are in accordance with ISO15-1981. The dimensions of the snap ring grooves and snap rings are in conformity with ISO464-1976.
Angular misalignment
Single row deep groove ball bearings have very limited capability to make self-alignment. The allowable angular misalignment between the inner and outer rings depends on the radial internal clearance of the running bearing, the bearing internal design and the forces and torques exering on it, while the max allowable angular error must be restricted in order to prevent from over stress arising. Because of the above-mentioned complicated relations among these factors, the exact value for the max angular misalignment can not be given, but under normal working conditions, it is usually between 2 and 10 minutes of radian. Precaution: the bearing noise level will be increased when the angular misalignment arise considerable between the inner and outer rings during bearings running.
Double row deep groove ball bearings can take 2 minutes of radian of angular misalignment. Large angular misalignment would increase the unacceptable load between the balls and grooves, so that bearing life is shortened.
Tolerances
HRB standard deep groove ball bearings are made to normal tolerance class P0. And high precision products of tolerance classes P6, P5, P4 and P2 can also be supplied.
Internal clearance
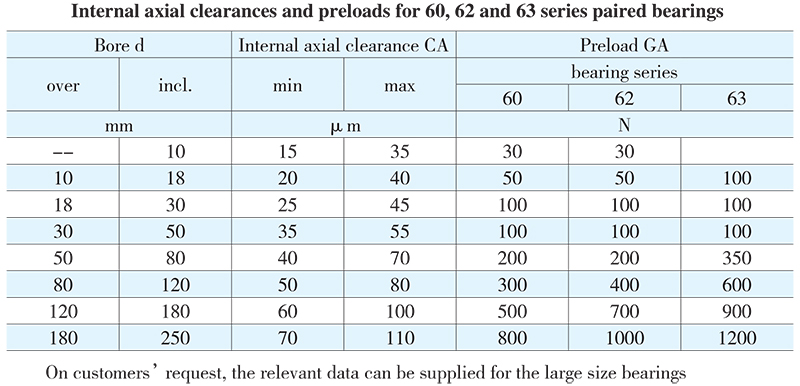
HRB ordinary deep groove ball bearings have C0 group internal clearance. These products with radial internal clearance larger or small than the normal can also be available. HRB double row deep groove ball bearings are usually manufactured to normal level radial internal clearance. Among them back-to-back or face-to-face paired bearings are often supplied with two ways: less axial internal clearance with designation suffix CA, or light preload with designation suffix GA shown in Table Internal axial clearances and preloads for 60, 62 and 63 series paired bearings are given in the below table.
Cages
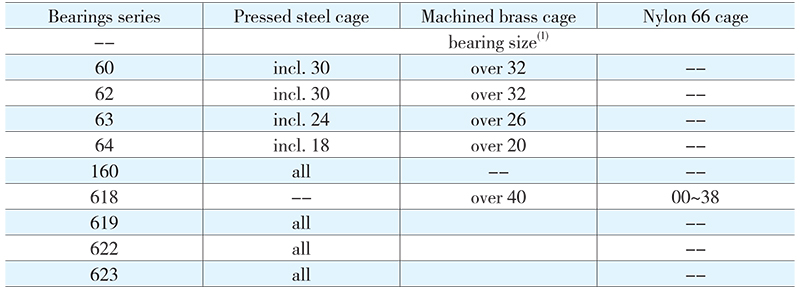
(1)The last two numbers in bearing designation
Usually deep groove ball bearings are fitted with a pressed ribbon cage, e.g.: nylon 66 or machined brass cages
Paired single row deep groove ball bearings
When the supporting capability of a single row deep groove ball bearing is not sufficient or a shaft has to be located in double directions with the same specified internal axial clearance, HRB can supply paired single row deep groove ball bearings on customer’s requirement. During manufacture, these bearings are matched in pairs so that an even load distribution will be obtained when mounted, in stead of using shims or other means to make adjustment. Depending on individual paired requirements, the following three arrangements of bearing pairs are available for different applications.
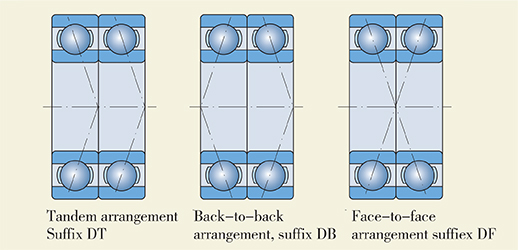
In tandem arrangement, the load actions lines are parallel each other, so that the paired bearings can only carry axial loads in one direction which are distributed in each bearing. When any axial loads in the reverse direction need to be carried, a third bearing has to be added and adjusted against them.
In back-to-back arrangement, the load action lines diverge at the bearing axis, so that axial loads can be carried in either direction, but only by one bearing of the paired bearings. This arrangement is a more rigid bearing arrangement which can also take tilting moment.
In face-to-face arrangement, the load action lines converge at the bearing axis, so that axial loads can be carried in either direction, but only by one bearing of the paired bearings. This arrangement can not accommodate tilting moment. In order to ensure a defined position order of paired bearings for ready mounting, a symbol ”V” is marked on the outer rings of each bearing pair. The bearing must be mounted in the order of its symbol ”V” so as to achieve satisfied operation. These bearings are packaged in each defined pair for delivery.
Speeds of bearing pairs
The speeds given in bearing tables are only foe single bearings. The bearing pair can reach an operating speed, about 20% lower than the allowable operating speed of the single bearing.
Load carrying capacity of bearing pairs
The basic dynamic load ratings and basic static load ratings given in bearing tables are only for single bearings. For bearing pairs, the basic dynamic load rating should be multiplied by 1.62, the basic static load rating multiplied by 2.
Expansion compensation for deep groove ball bearings
The boundary dimensions of these bearings are the same as relevant normal bearings, only additionally with circular grooves on the outer ring diameter surface which are filled with polymeric material of high expansion factor.
On design, the thermal expansion ratio of the polymeric material outside diameter must closely approach to that of the light metal bearing housing bore. Therefore, the bearings can be allowed greater expansion in wider temperature range without outer ring deformation when working in the light metal bearing housing.
While a deep groove ball bearing with expansion compensation is pressed into a bearing housing, never damage the polymeric material which is the key point. Hence, the inlet of the bearing housing bore has to be cornered 10 to 15°. And during mounting, tilting the bearing is not allowed; better to utilize the shown device to press it into the housing bore.
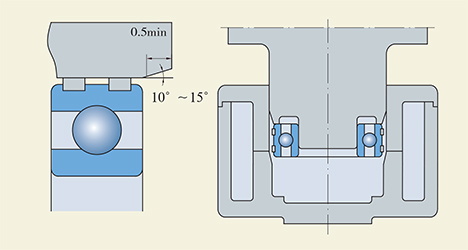
Heating or cooling mounting is not suitable for these bearings because the polymeric material would be spoiled. Additionally, the allowable load rating Cp (see bearing tables) of a bearing is decided on the basis of its outer ring strength. When selecting a bearing, the max load rating cannot be allowed to go beyond the Cp value.
In general, the C3 group internal clearance is adopted for the these bearings.
Double row deep groove ball bearings
The design of double row deep groove ball bearings is similar to that of HRB single row deep groove ball bearings, without filling slot, so that they can carry axial loads in either direction.
Equivalent dynamic load
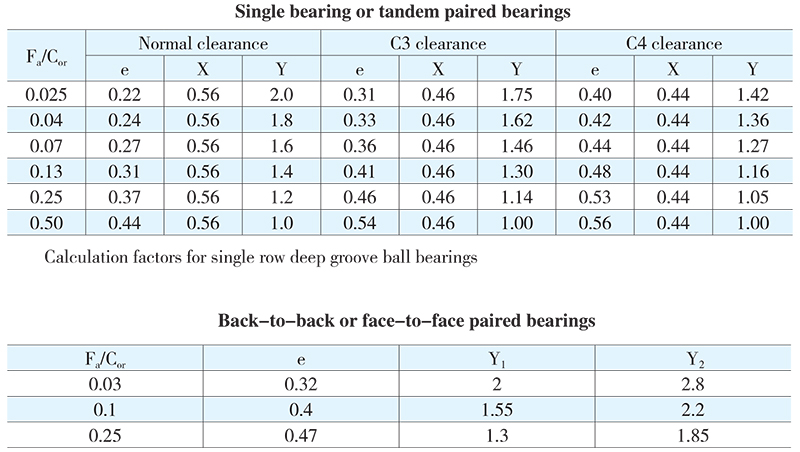
Deep groove ball bearings can generally carry radial and axial combined loads which have to be converted to equivalent dynamic load. The equivalent dynamic load not only depends on the ratio between the axial load and basic static load rating but also is under the influence of the radial internal clearance. The greater the radial internal clearance is, the greater the axial carrying ability becomes.
when Fa/Fr>e
P = XFr + YFa (KN)
when Fa/Fr ≤ e
P = Fr (KN)
For back-to-back or face-to-face paired bearings
when Fa/Fr>e
P = 0.75Fr + Y2Fa (KN)
when Fa/Fr ≤ e
P = Fr + Y1Fa (KN)
Where
P — equivalent dynamic load (KN)
Fr — radial load (KN)
Fa — axial load (KN)
X — radial load factor
Y, Y1, Y2 — axial load factors (KN)
Equivalent static load
The equivalent static load is defined as that of hypothetical static load, which would have the same influence on the totally constant deformation magnitude of the contact portion between the rolling elements taking most of the loads, and the ring as actual loads if applied.
For single bearing or tandem paired bearings
P0 = 0.6Fr + 0.5Fa (KN)
when P0<Fr, P0 = Fr (KN)
For back-to-back or face-to-face paired bearings
P0 = Fr + 1.7Fa (KN)
where P0 — equivalent static load (KN)
Radial load factor X and axial load factor Y for single row deep groove ball bearings
Catalog of Single row deep groove ball bearing
Catalog of Single row deep groove ball bearing with expansion compensation